Wireless Charging For Artificial Heart Pumps
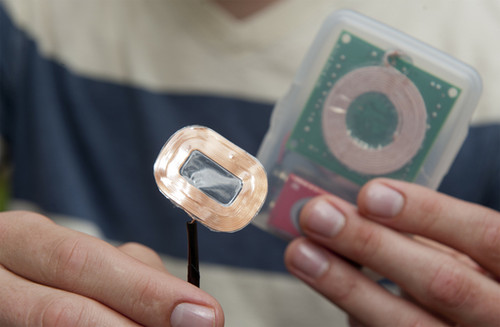
Ventricular assist device (VAD) is a minimally invasive artificial heart pump developed by the Houston-based Procyrion, offered when there`s a need for a heart transplantation and there’s no transplant available. A team of Rice University’s senior researchers have resolved the biggest VAD challenge – lack of stable battery backup by developing transcutaneous energy transfer or TET. The prototype cardiac charger version is to be placed a centimeter under the skin at a patient’s waist and contains a tiny coil and a battery, which can send the stored power to the VAD. The patient is to constantly wear in a belt-mounted external battery and coil to generate power and charge the transcutaneous coil, as the VAD can pump the heart for over three hours on a single charge. The Rice University researchers say the belt can be removed for a few minutes only, for example, for taking shower.
Via: gizmowatch.com
| Tweet |